What is Web Portal?
“Architecture begins where engineering ends.” Walter Gropious
Introduction
If a need for sharing resources drove the computer networks into being, same can be said for Web Portals (WPs) as well. Simply, it all began as a need to provide web services. With the expansion of the Internet in mid 1990’s due to the introduction of the Web browsers, it made WPs to become ‘must have it’ business activity of the companies at that time. All this, was mainly due to the desire of becoming a leader in the Internet market. Such euphorically decision “died down with the dot-com flameout in 2000 and 2001” (Wikipedia, 2015), which caused several companies to bankrupt, others to sell what it remained, and the rest to pull out themselves hardly from such rushed business decision. However, the moral of such bitter business experience was the fact that Yahoo!, MSN, and few others WPs have survived and proved to be very successful in business that deals mainly with providing services based on web.
The dot-com flameout, although it almost wiped out from the history of the Internet, didn’t mark the end of WP. Instead WP gained its true face and character, and became a much more respected business activity on the Internet, Intranet and Extranet. A diverse and big number of services offered by WPs made them being categorized into types dependable upon structure, content, design, business activity and whom they serve. Nowadays, the following WPs types exist: personal portals, corporate (intranet) portals, regional portals, web searching portals, business intelligence portals, e-Learning portals, e-Commerce portal, self-service portals, and many other types of WPs.
Technologies
WPs are n-tier networking infrastructure due to the fact that they provide dynamic content. In turn, this means that WPs should utilize an advanced technology for efficient access of data from external sources. That said, today among several existing technologies available for dynamic web based applications, the most famous and most used are JSP, ASP, (PHP), and CF.
Architectures
In comparison to WP technologies which mainly deal with Web Servers and scripting languages for data access, on the other side WP architectures deal with a set of mandatory core functionalities. Today, WPs are playing a crucial role in a process of providing Web-based applications. Based upon functionalities mentioned above, there are companies which are offering own web-based products to satisfy the needs and demands of businesses interested in designing, and deploying WPs. The most recognized and recommended WP Servers are: IBM’s WebSphere Portal, SAP’s mySAP Portal, Microsoft’s SharePoint Portal, Oracle’s Oracle9iApplicationServer Portal, Sun Microsystems & Netscape Alliance iPlanet Portal, and others.
Platforms
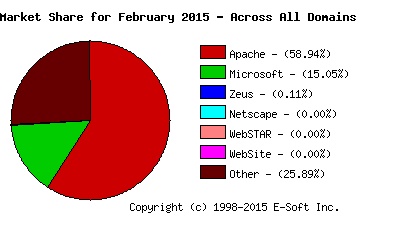
One of the important factors to consider when designing and deploying WP is the platform, which determines the NOS that the WP server will run on. It means if the WP runs on the Microsoft Windows Web Server 2008, then this WP is based upon Windows 2008 platform. When talking about OSs, then its good to mention that currently the most popular NOS are: MS Windows Server 2008/2012, Linux (distributors such as Red Hat, Suse, Debian, Mandrake, Caldera, etc.), UNIX (with available types such as IBM’s AIX, HP’s UX, Sun Microsystems Solaris), and Apple Mac OS X Server. Besides NOS, in order for the WP to be deployed requirement is to have a web server as well. Today’s most used web servers for running WPs are: IIS 8.0 for Microsoft platform, Apache 2.4.12 for UNIX/Linux platform, and WebObjects for Apple Mac platform.
Benefits
Because of wide range of services that can be offered through WPs, the list of benefits becomes very long. If we are allowed to categorize the benefits into business and consumer related, again we will be amazed of the enormous benefits that both categories are gaining from WPs. From the point of the business related benefits Guruge (2003) provides an excellent example with well-known company SAP:
Benefits that SAP is gaining from the WP such as increased productivity, improved user experience and individual efficiency, improved customer, improved partner, improved supplier relationships, and many others, provides the best example of business related benefits.
On the other side, consumer related benefits would be benefits gained by end users thorough access of web services such as instant messaging, e-mail, web hosting, e-commerce, e-banking, and many others. Another important benefit viewed from both business and consumer perspective is the one “related to applications running in a portal which increases the availability of common services and function.” (Ben-Natan, Gornitsky, Hanis, & Sasson, 2004)
Dear readers, hope you find this post informative.
peace and blessings,
Bekim
References:
Ben-Natan, R., Gornitsky, R., Hanis, T., & Sasson, O. (2004). Mastering IBM WebSphere Portal: Expert Guidance to Build and Deploy Portal Applications. Indianapolis, IN: Wiley Publishing, Inc.
Guruge, A. (2003). Corporate Portals Empowered with XML and Web Services. New York, NY: Elsevier Science.
Wikipedia. (2015, January 31). WP. Retrieved April 02nd, 2015, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_portal